In recent years, there has been a growing interest in adopting a whole foods, plant-based (WFPB) diet for its potential health benefits. This dietary approach emphasizes consuming plant-derived foods in their whole, unprocessed form. Let's delve into the science behind this diet and explore whether it might be the right choice for you.

Understanding the Whole Foods, Plant-Based Diet
The Whole Foods, Plant-Based Diet is not created by a single individual or entity; rather, it is a dietary approach that has evolved over time based on scientific research and the work of various experts in nutrition and health. While there isn't a specific creator, advocates and researchers, such as Dr. T. Colin Campbell, Dr. Caldwell Esselstyn, and Dr. Joel Fuhrman, have contributed significantly to the promotion and understanding of plant-based diets through their studies and publications. The movement has gained popularity as more research highlights the potential health benefits of emphasizing plant foods in one's diet.
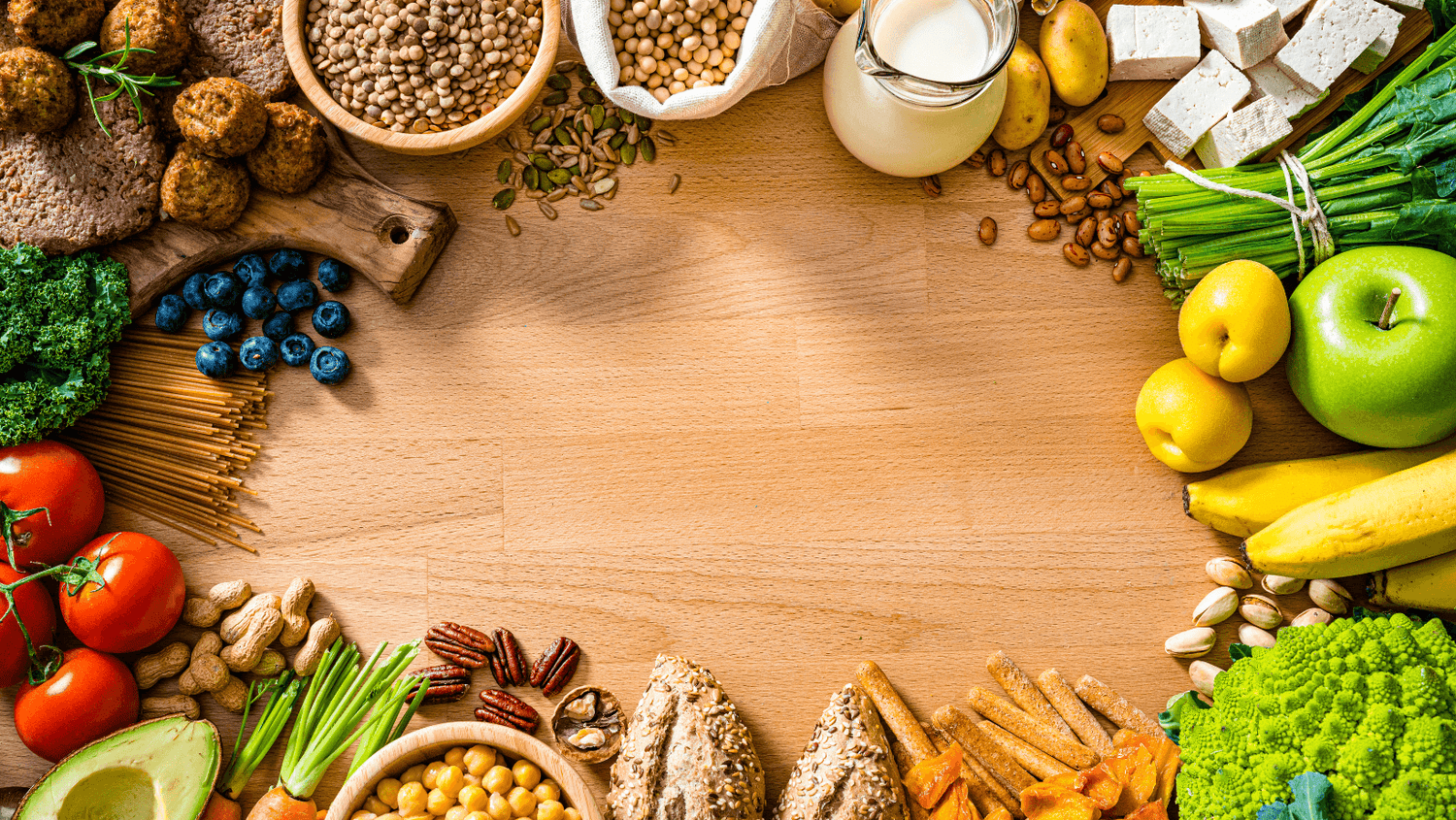
The whole foods, plant-based diet is centered around consuming minimally processed, nutrient-dense plant foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. This diet excludes or minimizes animal products and highly processed foods, aiming to harness the health-promoting properties of plant-based nutrition.

Principles of a Whole-foods, Plant-based Diet
While both Whole Foods, Plant-Based (WFPB) and vegetarian diets share a focus on plant-derived foods, there are notable differences between the two: WFPB emphasizes whole, minimally processed plant foods. The focus is on consuming foods in their natural state, with an avoidance of heavily processed items. Vegetarianism excludes meat and sometimes other animal products but may include processed vegetarian foods like meat substitutes, cheeses, and processed plant-based snacks.

Overall, the basic principles of WPFB are as follows:
- Emphasis on whole, minimally processed foods
- Limit or avoid animal products
- Focus on plants, including vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, seeds and nuts, which should make up the majority of what you eat
- Excludes refined foods such as added sugar, white flour and processed oils
- Particular attention is paid to food quality, with many supporters of the WFPB diet promoting locally sourced, organic foods wherever possible
How to Start a WFPB Diet
Embarking on a Whole Foods, Plant-Based (WFPB) diet involves making gradual and sustainable changes to your eating habits. Here are steps to help you get started:
- Learn about the principles of a WFPB diet. Understand which foods are encouraged and which are limited.
- Start by incorporating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes into your meals.
- Look for diverse and appealing plant-based recipes. Experimenting with new dishes can make the transition enjoyable.
- Pay attention to food labels to identify hidden animal products or processed ingredients.
- If needed, consult with a registered dietitian or nutritionist who specializes in plant-based diets to ensure you meet your nutritional needs.

Health Benefits of a WFPB Diet
Many studies have shown that adopting a Whole Foods, Plant-Based (WFPB) diet has been associated with various health benefits. Here are some key advantages:
- Heart Health: Studies have shown that a WFPB diet may contribute to lower cholesterol levels, reduced blood pressure, and a decreased risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Easy Weight Management: The high fiber content in plant-based foods can aid in weight management by promoting satiety and regulating calorie intake.
- Blood Sugar Control: Some evidence suggests that a WFPB diet may improve insulin sensitivity and help manage blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a whole foods, plant-based diet offers numerous health benefits and has gained popularity for its potential to prevent and manage chronic diseases. However, it's essential to approach this dietary choice with informed decisions, considering individual health needs and potential challenges. Consultation with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance for those considering adopting a WFPB lifestyle.